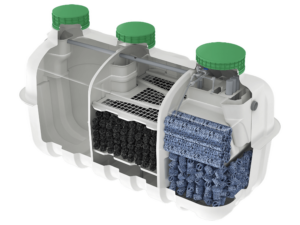
As a New York homeowner, you might not think much about what happens after you flush the toilet or drain the sink. However, if your home uses a septic system, it’s a crucial part of your daily life. Traditional septic systems, widely used across New York, especially in non-municipal areas, play a significant role in managing household wastewater. But, it’s important to understand their environmental impact.
Septic systems are designed to treat wastewater from your home using natural processes. While they are effective in many ways, traditional systems can have limitations in fully protecting the environment. Issues like soil absorption capacity and nutrient runoff can pose challenges, potentially leading to groundwater contamination and other environmental concerns.
In New York, where protecting our diverse ecosystems is vital, understanding these environmental implications is crucial. The state has implemented stringent regulations overseen by the New York State Department of Health to ensure septic systems function effectively while minimizing their ecological footprint.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll explore how modern advancements in septic technology, like Individual/Alternative Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems (I/A OWTS), are addressing these environmental challenges. These advanced systems offer improved wastewater treatment capabilities, significantly reducing the potential adverse effects on our environment.
This article aims to inform and educate you, as a responsible homeowner, about the vital role your septic system plays in environmental conservation. Understanding this will not only help you make informed decisions about your home’s wastewater management but also contribute to preserving New York’s beautiful and diverse natural habitats.
Understanding Septic Systems: Components and Function
A septic system may be out of sight, but it shouldn’t be out of mind, especially considering its environmental role. Let’s break down how a traditional septic system works and its key components:
The Basics
At its core, a septic system collects wastewater from your home (from toilets, sinks, showers, and laundry) and treats it on-site. This is different from a public sewer system, where wastewater is sent to a central treatment facility.
Key Components of a Septic System
Septic Tank
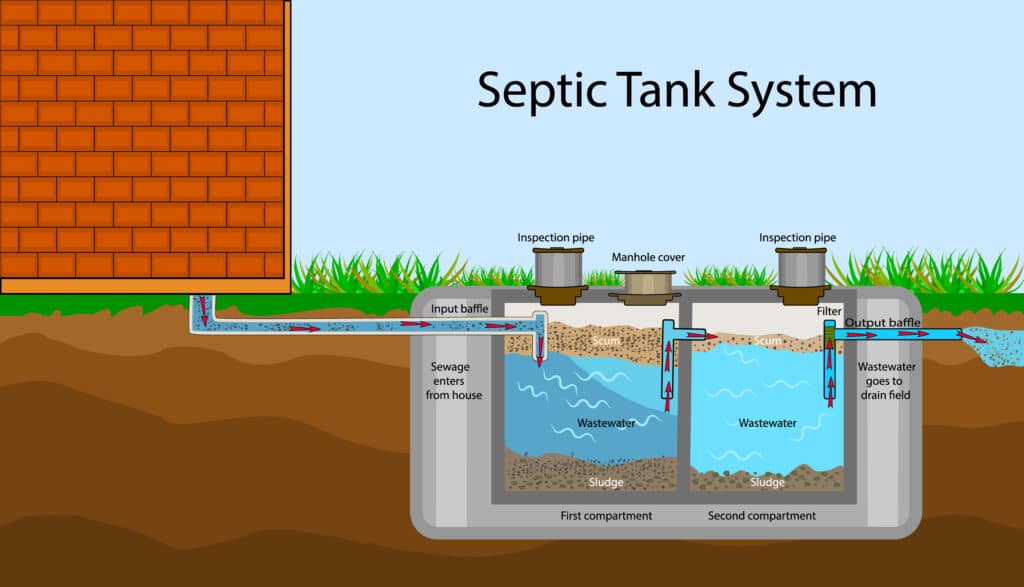
This buried, watertight container is where the initial treatment happens. Wastewater flows into the tank, where solids settle at the bottom, and fats, oils, and greases float to the top. Bacteria in the tank begin breaking down this material.
Drainfield
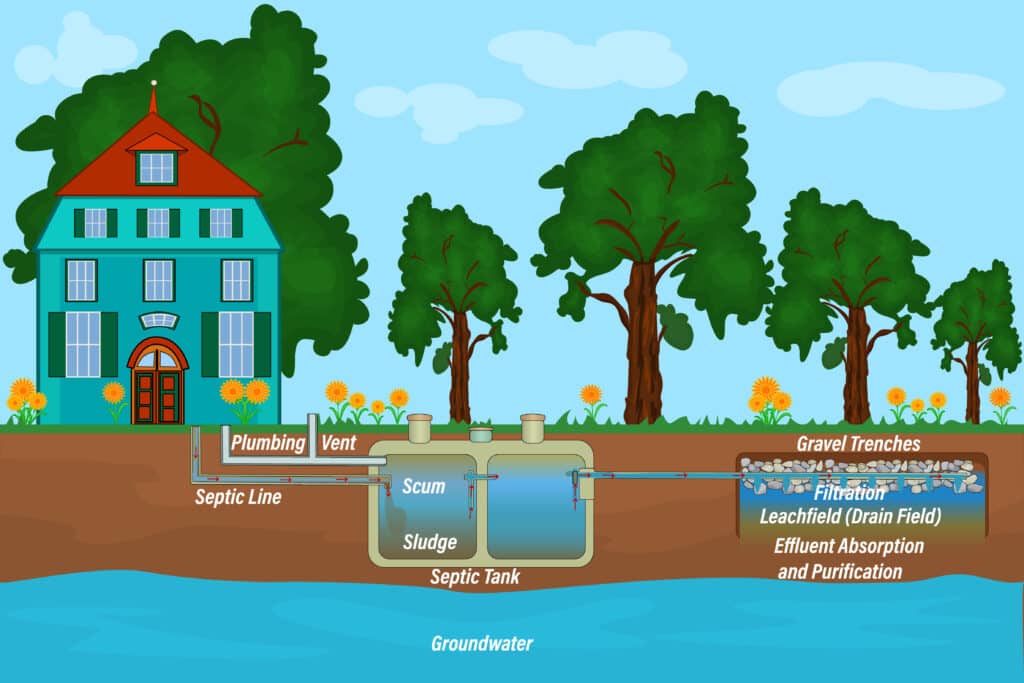
Also known as the leach field, this area receives the liquid effluent from the septic tank. It then percolates through the soil, which provides further treatment by removing harmful bacteria, viruses, and nutrients.
The Process
After the wastewater enters the septic tank, the separation process starts. The solids, or sludge, stay at the tank’s bottom. The middle layer, known as effluent, is mostly clear and moves out into the drainfield.
In the drainfield, the effluent is distributed through pipes into the soil. The soil acts as a natural filter, helping to remove harmful substances, eventually returning the treated water to the groundwater system.
Environmental Concerns
Traditional septic systems are generally effective. However, they can struggle to fully remove certain pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorus. This can lead to nutrient overloading in nearby water bodies, causing issues like algae blooms and affecting aquatic life.
Additionally, if a septic system is poorly maintained or overused, it can lead to groundwater contamination, which poses a significant risk to both human health and the environment.
The Importance of Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including pumping out the septic tank every 3-5 years, can prevent system failures and extend its lifespan.

Being mindful of what goes down the drain is also crucial. Non-biodegradable materials, chemicals, and excessive water use can strain the system.
In the next section, we’ll explore the regulations and standards in New York that govern these systems, helping to mitigate their environmental impact. As we move towards more environmentally-friendly options like I/A OWTS, understanding these basics lays the groundwork for appreciating the advancements these new systems bring.
Regulations and Standards in New York for Septic Systems
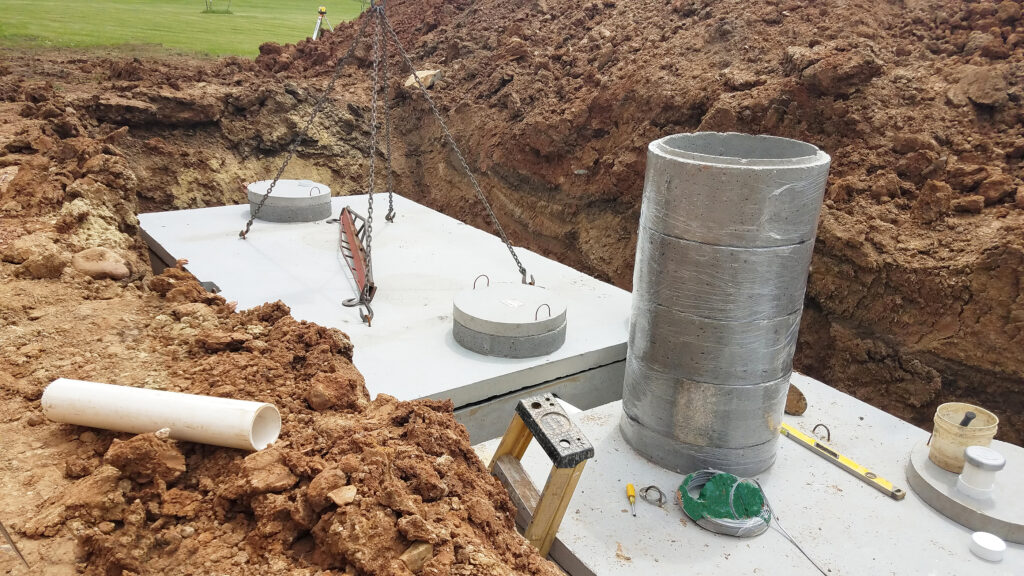

Navigating the rules and regulations for septic systems in New York is key to ensuring both environmental protection and system efficiency. Here’s what homeowners should know:
State and Local Regulations
In New York, the management of septic systems is governed by both state and local authorities. The New York State Department of Health sets the overarching guidelines.
Local health departments may have additional, more specific requirements, tailoring regulations to the needs of their specific communities.
Design and Installation Standards
New York State provides detailed standards for the design and installation of septic systems, ensuring systems are built to handle the specific wastewater needs of a home while protecting the environment.
Considerations in design include soil type, property size, and proximity to water bodies, to prevent issues such as groundwater contamination.
Inspection and Maintenance Requirements
Regular inspections by certified professionals are crucial for the longevity of septic systems and environmental safety.
Homeowners are typically required to pump out their septic tank every few years, depending on usage, to prevent overflows and backups.
Upgrading to I/A OWTS
New York encourages the adoption of Innovative/Alternative Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems (I/A OWTS), recognizing the limitations of traditional systems in environmental protection.
I/A OWTS provide superior treatment, significantly reducing pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are problematic in traditional systems.
Financial Assistance Programs
New York State offers financial assistance through programs like the Septic System Replacement Fund, to help homeowners with the costs of maintaining, repairing, or upgrading to environmentally friendly systems like I/A OWTS.
These programs are particularly geared towards supporting the transition to more environmentally friendly options like I/A OWTS.
Permitting Process
Installation or upgrade of a septic system requires adherence to a permitting process, ensuring compliance with environmental and health standards.
This process is crucial for ensuring new or modified systems meet current standards and effectively contribute to environmental protection.
By understanding and complying with these regulations, and considering advanced treatment options like I/A OWTS, homeowners can significantly contribute to safeguarding New York’s diverse ecosystems. The shift towards more efficient and environmentally-friendly septic systems is a commitment to a sustainable and ecologically responsible future.
Design and Installation: What Homeowners Need to Know
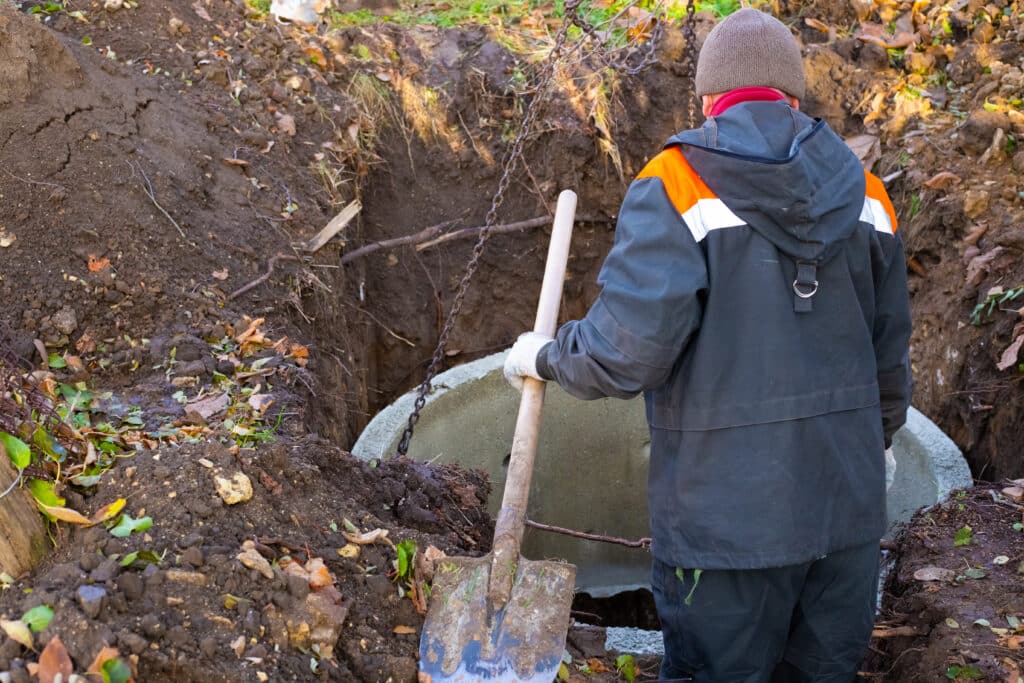

When it comes to the design and installation of septic systems in New York, homeowners should be well-informed to ensure their system is not only compliant but also environmentally friendly. Here are the key aspects to consider:
Site Evaluation
Soil Analysis
The type of soil on your property is crucial. It affects how well wastewater can be filtered and absorbed.
Property Assessment
The size of your land, the proximity to water bodies, and the location of neighboring properties are all considered to determine the best placement and type of system.
Choosing the Right System
Conventional Systems
Traditional septic systems are suitable for many properties but may have limitations in nutrient filtering.
I/A OWT
These advanced systems offer better treatment and are ideal for environmentally sensitive areas or properties with limited space or poor soil conditions.
Design Considerations
Capacity Planning
The system should be designed to handle the specific waste output of your household, based on factors like the number of bedrooms and occupants.
Environmental Compliance
The design must meet state and local regulations, focusing on reducing environmental impact, particularly in nutrient-sensitive areas.
Installation Process
Professional Installation
Hiring certified and experienced professionals is key to ensuring that the system is installed correctly and efficiently.
Inspection and Approval
After installation, the system must be inspected and approved by local health authorities to ensure it meets all regulations and standards.
Cost and Planning
Budgeting
Understanding the costs, including installation, maintenance, and potential upgrades, is essential for effective financial planning.
Financial Assistance
Explore state and local programs that offer financial aid for septic system installation, particularly for environmentally friendly systems like I/A OWTS
By taking these factors into account, homeowners can ensure their septic system not only serves their household efficiently but also contributes positively to New York’s environmental health. Embracing advanced systems like I/A OWTS can further this impact, offering a more sustainable solution to wastewater management.
Operation and Maintenance of Septic Systems
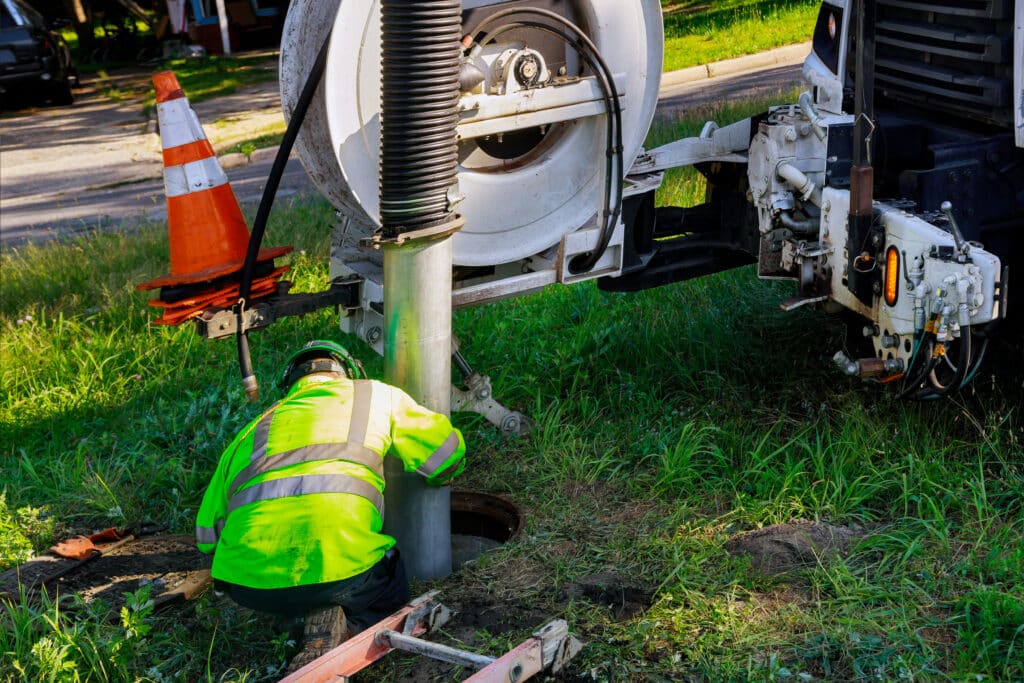

Proper operation and maintenance are critical for the longevity and efficiency of your septic system, and for minimizing its environmental impact. Here’s what homeowners in New York need to know:
Regular Maintenance Routines
Pumping the Septic Tank
This should be done every 3-5 years, depending on the size of the tank and household usage.
Inspections
Have your system inspected by a professional regularly to catch and address any potential issues early.
Best Practices for Everyday Use
Water Efficiency
Using water efficiently reduces the load on your septic system. Fix leaks and consider water-saving fixtures.
Waste Disposal
Be cautious about what goes down your drains. Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items and harmful chemicals.
Recognizing and Addressing Problems
Signs of Trouble
Slow drains, unpleasant odors, or wet areas around the drain field can signal issues.
Professional Assistance
If you notice any problems, seek professional help promptly to prevent further damage.
Environmental Considerations
Nutrient Runoff
Be aware of the potential for nutrient runoff from your system, which can impact local waterways.
Landscaping
Proper landscaping around your drain field can enhance the environmental performance of your system.
Upgrading to I/A OWTS
Considering an Upgrade
If your current system is aging or if you’re concerned about its environmental impact, consider upgrading to an I/A OWTS.
Benefits of Advanced Systems
I/A OWTS provide better treatment and are more efficient in reducing pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorus.
Community and Environmental Impact
Responsibility as a Homeowner
Properly maintaining your septic system is not just about home care; it’s a commitment to your community and the environment.
Contribution to Water Quality
A well-maintained septic system contributes to the overall health of New York’s water bodies and ecosystems.
By following these guidelines, homeowners can ensure their septic systems function effectively, avoid costly repairs, and play a part in protecting the environment. Remember, your septic system is a vital component of your home and the broader ecological system of New York.
Costs and Financing: Installation and Replacement
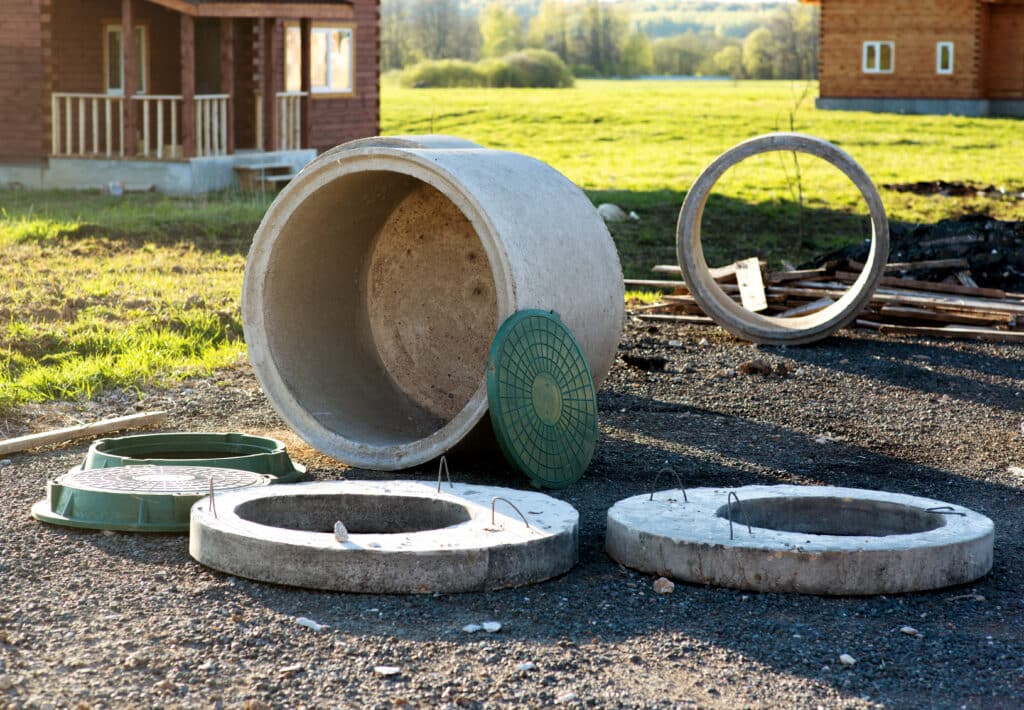

Understanding the financial aspects of installing and maintaining a septic system is crucial for homeowners in New York. Here’s a breakdown of what to expect and available financial assistance:
Installation Costs
Conventional Systems
The cost for a new conventional septic system varies, but the average in New York is about $15,000 and $18,000 for a 3-bedroom house.
I/A OWTS
These advanced systems may cost more upfront due to their sophisticated technology and installation requirements, but many (if not all) of these costs can be offset through extensive grant and rebate programs.
Maintenance and Repair Expenses
Regular Maintenance
Budget for routine maintenance, including pumping and inspections, which are essential for system longevity.
Unexpected Repairs
Set aside funds for potential repairs. A well-maintained system is less likely to incur costly emergency repairs.
Financing Options and Assistance Programs
State Programs
New York offers financial assistance through programs like the Septic System Replacement Fund, which helps with the costs of replacing aging or failing systems.
County Grants
Some counties in New York provide grants to reimburse homeowners for a portion of their septic system projects.
Cost-Effective Upgrades
Long-Term Savings
While the initial cost of an I/A OWTS is higher, the long-term environmental and efficiency benefits can lead to savings.
Investment in Property Value
Upgrading to a more efficient system can increase your property’s value and appeal.
Budgeting for Your Septic System
Planning
Include septic system expenses in your home maintenance budget.
Exploring Assistance
Research local and state programs for potential financial support, especially if considering an upgrade to an I/A OWTS.
Environmental Investment
Balancing Cost and Impact
While managing costs is important, consider the environmental benefits and long-term sustainability of your septic system choice.
Community Benefits
Investing in a more efficient and environmentally friendly system contributes to the overall health of New York’s ecosystems.
For New York homeowners, being financially prepared for the installation, maintenance, and potential upgrade of a septic system is a key part of responsible homeownership. Exploring available financial assistance and considering the long-term benefits of efficient systems like I/A OWTS can make this investment more manageable and rewarding.
Certification of Septic System Designers and Installers in New York

For homeowners in New York, ensuring that your septic system is designed and installed by certified professionals is crucial for both functionality and compliance with environmental standards. Here’s what you need to know about the certification process:
Certification Requirements
Education and Training
Designers and installers must complete specific education and training as mandated by New York State.
Examinations
They are required to pass written, oral, and/or practical examinations to demonstrate their competency in septic system design and installation.
State Sanitary Code
Standards Compliance
The certification ensures that professionals are well-versed in the State Sanitary Code, which governs the design and installation of septic systems in New York.
Environmental Protection
This knowledge is crucial for installing systems that meet environmental protection standards, especially important in ecologically sensitive areas.
Finding Certified Professionals
Verification
Homeowners should verify the certification of designers and installers through the New York State Department of Health or local health departments.
Recommendations
Seeking recommendations and checking reviews can also be a valuable part of finding a reliable and certified professional.
Continuing Education
Updates in Regulations and Technologies
Certified professionals are required to keep up-to-date with the latest regulations and advancements in septic system technologies, including I/A OWTS.
Ongoing Training
This ensures they remain competent in modern, environmentally-friendly septic system practices.
Impact on Homeowners
Quality Assurance
Hiring certified professionals provides assurance of quality and compliance with state and local regulations.
Long-term Benefits
Proper design and installation by certified professionals can extend the life of your septic system and prevent costly repairs and environmental damages.
Role in Environmental Stewardship
Expert Guidance
Certified designers and installers can provide expert guidance on the best system for your property, considering environmental impact and efficiency.
Contribution to Ecosystem Health
Their expertise plays a significant role in maintaining the health of New York’s diverse ecosystems, particularly when installing advanced systems like I/A OWTS.
For homeowners, understanding the importance of certification in septic system design and installation is key to ensuring a properly functioning, environmentally responsible, and compliant wastewater treatment system on their property.
Filing Concerns and Complaints

As a homeowner in New York, if you encounter issues with your septic system or with the services provided by septic professionals, it’s important to know how to file concerns or complaints effectively. Here’s a guide to navigating this process:
Initial Steps
Contact Local Authorities
Start by reporting your concerns to your town hall, as they are often the first point of contact for septic system issues.
Documentation
Keep detailed records of your concerns, including dates, descriptions of the issue, and any communications with service providers.
State-Level Reporting
New York State Department of Health
If your issue is not resolved at the local level, you can escalate it to the New York State Department of Health, particularly for issues related to system functionality or public health concerns.
Contact Information
Reach out to the Department of Health’s Center for Environmental Health for guidance on the complaint process.
Consumer Protection Agencies
Attorney General’s Office
For disputes or grievances with septic system companies, you can contact the New York State Attorney General’s Office.
Better Business Bureau
Filing a complaint with the Better Business Bureau can also help address issues related to service quality or business practices.
Seeking Legal Advice
Consultation
In complex cases, especially those involving contractual disputes or significant financial implications, consulting a legal professional can be beneficial.
Legal Action
They can guide you on the feasibility of taking legal action and the steps involved.
Community Resources
Homeowner Associations
If you’re part of a homeowner association, they may offer support or advice, as septic issues can often affect multiple residents in the area.
Online Forums and Support Groups
Engaging with online communities can provide insights and shared experiences from other homeowners who have faced similar issues.
Preventive Measures
Regular Maintenance
Keeping up with regular septic system maintenance can prevent many issues and reduce the likelihood of needing to file a complaint.
Informed Hiring
Researching and hiring certified and reputable septic system professionals can also minimize potential problems.
By understanding these steps and knowing where to turn for help, homeowners can more effectively address concerns related to their septic systems, ensuring their rights are protected and their living environment remains safe and healthy.
Environmental Impact and Advanced Treatment Options

In New York, the shift towards environmentally sustainable septic systems is not just a trend, but a necessity. Understanding the environmental impact of traditional septic systems and the benefits of advanced treatment options is crucial for homeowners. Here’s an overview:
Limitations of Traditional Septic Systems:
Nutrient Pollution
Conventional systems can contribute to nutrient pollution in water bodies, leading to problems like algae blooms.
Groundwater Contamination
Inefficient treatment of wastewater can lead to the contamination of groundwater, a critical issue for public health and ecosystems.
Advantages of I/A OWTS:
Enhanced Treatment
These systems offer superior treatment, effectively reducing pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorus.
Eco-Friendly Design
I/A OWTS are designed with the environment in mind, minimizing the ecological footprint of wastewater treatment.
State Initiatives and Regulations:
New York State promotes the adoption of I/A OWTS through various initiatives and financial assistance programs. For more detailed information on environmental considerations for septic systems, especially within the New York City watershed, visit the New York State Department of Environmental Protection at www.nyc.gov/dep.
Choosing the Right System:
Assessment and Planning
Homeowners should assess their property’s needs and environmental conditions when choosing a septic system.
Professional Consultation
Consulting with certified septic system professionals can help in selecting the most suitable and sustainable option.
Community and Ecological Benefits:
Protecting Water Bodies
By reducing nutrient runoff and pollution, advanced systems help protect New York’s lakes, rivers, and groundwater.
Sustainable Living
Adopting environmentally friendly septic systems aligns with sustainable living practices, contributing to the health of local ecosystems.
Future Trends and Innovations:
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development in septic system technologies promise more efficient and less intrusive solutions.
Environmental Awareness
Increasing awareness among homeowners about their role in environmental stewardship is driving the demand for advanced treatment systems.
By understanding the environmental impact of their septic systems and considering advanced treatment options like I/A OWTS, homeowners in New York can play a significant role in preserving the state’s natural beauty and ensuring a sustainable future for the coming generations.
New York Septic System FAQs

Here are some of the most common questions we see regarding septic systems in New York State:
Who regulates septic systems in NY?
The regulation of septic systems in New York is overseen by the New York State Department of Health. The department administers the rules and regulations pertaining to septic systems throughout the state, including the certification of septic system designers and installers, on-site inspections, and addressing concerns and complaints related to septic systems.
In addition, septic systems within the New York City watershed must also be approved by the city’s Department of Environmental Protection, Division of Water Resources. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation is also involved in the regulation of septic systems, particularly in the inspection, measurement, and pumping out of septic tanks by licensed septage waste transporters.
Are plastic septic tanks legal in NY?
Yes, plastic septic tanks are legal in New York. According to the New York Codes, Rules and Regulations, fiberglass and polyethylene tanks are permitted, but they must meet specific requirements, such as being watertight and constructed of durable material not subject to corrosion, decay, frost damage, or cracking.
What is the cheapest septic system to put in?
The cost of septic systems varies based on the type, size, and specific property requirements. Traditional anaerobic septic systems are generally less expensive than advanced systems like I/A OWTS, however the availability of extensive grant and rebate programs, especially in New York State, can make the advanced options more affordable, or sometimes completely free to install. Companies like Bridgewater
Can you sell a house in NY with a failed septic?
Yes, you can sell a house in New York with a failed septic system. However, there are certain considerations and caveats to be aware of. Selling a home with a problematic septic system is not straightforward, and it may impact the property’s market value and the pool of potential buyers.
In some cases, selling the house “as is” to a cash buyer or real estate investor who can handle the necessary repairs may be a viable option. It’s important to disclose the issue to potential buyers and seek advice from a licensed real estate agent to understand the potential impact on the home’s market value.
Additionally, local laws and regulations should be taken into account, as some states or municipalities may have restrictions on selling a home with a failed septic system
These FAQs highlight key considerations for homeowners in New York regarding the regulation, types, costs, and legal aspects of septic systems. For more detailed information, consulting with local health departments and certified septic system professionals is recommended.